Scurvy has an interesting history and is caused by a lack of vitamin C. Scurvy was a widespread ailment among sailors and James Lind discovered in 1747 that the only foods that could cure it were oranges and lemons.
Although vitamin C can be synthesized by animals, scurvy was caused in guinea pigs by Axel Holst and Theodor Frölich. Charles Glen King discovered vitamin C in 1932 and Norman Haworth figured out its chemical composition in 1933 (Carpenter, 2012).
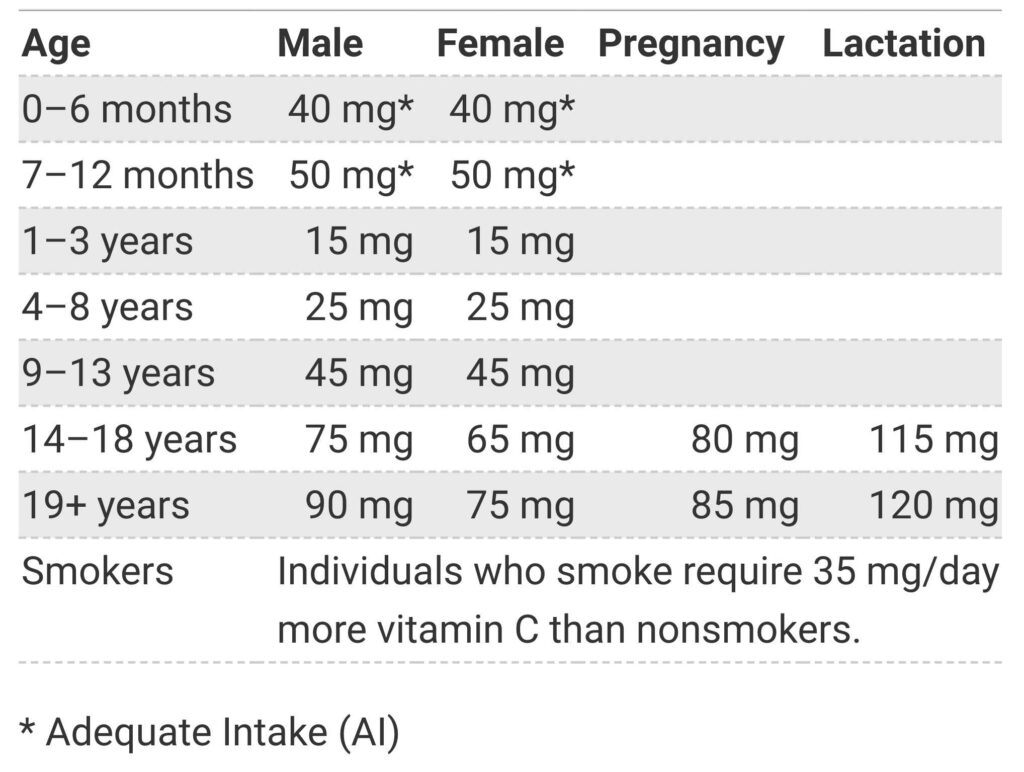
Importance, use, and required amount of vitamin C.
Humans cannot make vitamin C, which is a water-soluble vitamin (unlike other animals). It is essential for collagen synthesis, enzymatic processes, and control of gene expression (Naidu, 2003). It also has strong antioxidant properties (Buettner, 1993). A higher level of vitamin C can reduce the incidence of stroke, coronary heart disease, and hypertension according to studies (Morelli et al., 2020). Vitamin C supplementation has been shown to help shorten the duration of the common cold, but not to reduce the risk of illness (Rondanelli et al., 2018). There is no scientific evidence that taking high doses of vitamin C in adulthood can be harmful or poisonous. Unabsorbed vitamin C in the gastrointestinal system can cause diarrhea, nausea, abdominal cramps, and other gastrointestinal disturbances due to its osmotic impact (Jacob & Sotoudeh, 2002a). For those 19 years of age and older, the Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) is 75 mg for women and 90 mg for men. However, the daily need for vitamin C rises to 85 mg during pregnancy and 120 mg during breastfeeding. A balanced diet, which should include foods high in vitamin C such as citrus fruits, kiwifruit, strawberries, broccoli, and tomatoes, is therefore essential to meet these daily requirements and maintain good health (Levine et al., 2001).
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) of Vitamin C
1. Skin that is dry and damaged
Significant amounts of vitamin C are found in healthy skin, and these compounds protect the skin from oxidative damage from the sun and exposure to other harmful pollutants such as environmental contaminants (Pullar et al., 2017; Podda et al., 1998). In addition, it supports the synthesis of collagen, which maintains the youthful appearance of the skin (Duarte et al., 2009). According to studies, those who consume more vitamin C have better quality skin overall, while people who consume less vitamin C are 10% more likely to have dry and wrinkled skin (like et al., 2016). However, it is important to note that low vitamin C is only one of many things that can lead to dry and damaged skin (Cosgrove et al., 2007).
2. Simple bruises
A bruise is a discoloration that occurs when blood vessels under the skin burst, allowing blood to seep into the surrounding tissue. If you bruise easily, you may be deficient in vitamin C (Hirschmann & Raugi, 1999a). This vitamin is necessary for the synthesis of collagen, which maintains the health and strength of the skin, bones, and other tissues. Vitamin C deficiency can damage blood vessels and lead to insufficient collagen production, which increases the risk of bruising (Pimentel, 2003a).
3. Slow healing injuries

Vitamin C deficiency causes our body to produce collagen more slowly, which slows down wound healing (Galimberti & Mesinkovska, 2016). According to recent studies, individuals with persistent wounds that do not heal are more likely to be vitamin C deficient. Old wounds may reopen in certain acute cases of vitamin C deficiency, increasing the possibility of infection (Lazareth et al., 2007).
Reopening of previous wounds or slow wound healing are advanced indicators of insufficiency that may increase the risk of infection (Fain, 2005a). Thus, maintaining the level of vitamin C in our body at an optimal level promotes faster healing of wounds and reduces the possibility of infection (Hirschmann & Raugi, 1999a).
4. Gums that swell and bleed
Not having enough vitamin C in the body can weaken and irritate the gums, making the blood vessels more prone to bleeding. According to Olmedo et al. (2006), this can cause the gums to be red, swollen, and bleed. In severe cases of vitamin C deficiency, the gums can even turn red. Over a long period of time, unhealthy gums can compromise the integrity of the teeth (Larralde et al., 2007; Fain, 2005a).
Therefore, it is essential to ensure a sufficient supply of vitamin C through a nutritious and well-balanced diet.
5. Excruciatingly inflamed joints

Did you know that a lack of vitamin C can also cause problems with the connective tissue that makes up your joints?
This tissue is rich in collagen. To keep your joints healthy and functioning properly, you need to consume adequate amounts of vitamin C (Tamura et al., 2000).
6. Insufficient immunity
A robust immune system reduces the risk of serious infections such as pneumonia, and vitamin C is essential for this (Johnston et al., 2014). According to scientific research, vitamin C accumulates inside several types of immune cells, improving their ability to fight infections and fight diseases (Carr & Maggini, 2017).
It is important to note that scurvy, a disease caused by vitamin C deficiency, often leads to a weakening of the immune system. This can lead to increased susceptibility to infections and, worse, mortality if untreated (Pimentel, 2003a). For the proper functioning of the immune system, it is recommended to consume enough vitamin C in the diet.
7. Anemia Iron deficiency
Iron deficiency anemia and vitamin C are significantly correlated. By reducing iron absorption from plant foods and adversely affecting iron metabolism, low levels of vitamin C can exacerbate iron deficiency anemia (Teucher et al., 2004). (Lane & Richardson, 2014). Vitamin C deficiency also increases the possibility of excessive bleeding, which can result in anemia (Agarwal et al., 2015).
Get your vitamin C levels checked if you have iron deficiency anemia and there are no obvious reasons why.
8. Exhaustion

Inadequate consumption of vitamin C can result in a number of health problems. Early signs of vitamin C deficiency include fatigue and depression (Maggini et al., 2010). Several symptoms may appear before the deficit reaches its peak (Levine et al., 1996).
Although irritability and exhaustion are among the initial symptoms, they can usually be relieved by taking more vitamin C each day (Levine et al., 1996).
9. The link between oxidative stress and chronic inflammation
One of the most important antioxidants is vitamin C, which prevents free radicals from damaging cells.
Heart disease, oxidative stress, and inflammation have all been associated with low vitamin C intake (Helmersson et al., 2008; Moser & Chun, 2016). According to a study, people with low blood levels of vitamin C had a 40% higher risk of developing heart failure within 15 years compared to those with high levels (Pfister et al., 2011).
What foods contain the most vitamin C?
Vitamin C is essential for the growth, development, and repair of our body. According to Jacob and Sotoudeh (2002b), women need 75 milligrams of vitamin C per day, while men should have 90 mg per day. However, it is important to note that the body may require more vitamin C due to a number of conditions, including pregnancy, smoking, and illness (Jen & Yan, 2010; Gariballa & Forster, 2009). Fortunately, vitamin C is present in a wide variety of delicious foods.
Some of the best places to get vitamin C are:
Mandarins Grapefruits
Lemons
Kiwi berry
Papaya
bell peppers
Tomatoes with broccoli.
Acerola cherry
Blackcurrant Guava
Parsley, sweet red pepper and
By including these foods high in vitamin C in your diet, you can be sure you’re getting your recommended daily intake of this important component.
When vitamin C is supplemented

Evidence suggests that vitamin C may reduce the duration or intensity of colds, despite conflicting findings about its effectiveness in treating the common cold (Bucher & White, 2016). However, it is not certain whether vitamin C can ward off colds. It has been shown to reduce the duration and intensity of colds, but not their frequency.
Regarding vitamin C and infections, traditional medicine has historically depended on eminence-based treatment (based on physician opinion) rather than evidence-based treatment (Hemilä & Chalker, 2022).
Expensive urine?
It is not uncommon to hear critics suggest that supplementation is a waste of money and liken it to “expensive pee.” It’s normal to question the effectiveness of supplements, but it’s also important to remember that absorption is a key factor in how effective they are. It is important to follow certain guidelines to maximize the body’s absorption of these supplements if you want to make sure you are getting the most value from your purchase. Premium items should also be considered when purchasing any supplement.
Types of supplemental vitamin C
Liposomal vitamin C
It may surprise you that the optimal form of vitamin C is liposomal vitamin C. Most patients with severe vitamin C deficiency also have a problem with intestinal malabsorption. Liposomal vitamin C helps to solve this problem and ensures that your body receives the necessary amount of vitamin C for optimal performance (Gopi & Balakrishnan, 2020).
Vitamin C
After doing extensive research, I have come to the conclusion that ascorbic acid is the best choice for supplemental vitamin C due to its affordability and effectiveness. According to my research, ascorbic acid is a readily available vitamin C supplement that is simple and very useful (Johnston & Luo, 1994).
Bioflavonoids and vitamin C
It is possible that the combination of vitamin C and bioflavonoids may have a more significant effect on health. According to studies, the combination of these two nutrients can have an additive effect that increases their effectiveness. So think about including foods high in vitamin C and bioflavonoids in your diet if you want to boost your health (West et al., 2020).
weakened vitamin C
A supplement known as “buffered vitamin C” mixes ascorbic acid with a mineral salt, most commonly calcium. This special blend contributes to the supplement’s ability to withstand pH fluctuations and be gentler on the stomach. For people who have sensitive stomachs or experience digestive issues when taking regular vitamin C supplements, buffered vitamin C is a common choice (Cerullo et al., 2020).
Improvement proposal
180 cards of natural factors Vitamin C
This vitamin C is not like others. Natural elements To unlock the true potential of vitamin C, it is supplemented with citrus bioflavonoids and rose hips, nature’s secret for increased absorption. Together, they maximize the absorption of vitamin C in the body, protect the body from free radicals, maintain the integrity of collagen, and strengthen capillaries.
180 capsules of New Roots Herbal Vitamin C3
With eight forms of buffered vitamin C and other nutraceuticals for optimal health, Vitamin C& is a complete source of vitamin C. It blends ascorbyl palmitate with mineral ascorbates to provide a full range of antioxidant benefits, boost the immune system, and restore electrolytes. Each capsule has the antioxidant equivalent of three cups of green tea.
Vitamin C Crystals, 1000mg, 500g Powder, Natural Factors
The antioxidant vitamin C is well known for being essential for keeping teeth, gums, bones, and cartilage in good condition. Natural elements With 1000 mg of vitamin C per ¼ teaspoon, vitamin C crystals are an excellent source of the vitamin. The rapid dissolution of these crystals in liquid facilitates maximum absorption.
They are also excellent for strengthening teeth and bones, promoting wound healing, boosting the immune system, and improving blood circulation and the appearance of varicose veins.
Conclusion
Throughout the body, vitamin C is essential for tissue growth and repair.
It enables the synthesis of collagen, a protein that maintains the health of blood vessels, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, and skin. In addition, vitamin C is essential for both wound healing and strong teeth and bones.

Vitamin C is a key nutrient with a wide range of benefits for overall health. Its role goes beyond simply preventing scurvy to influencing various physiological processes necessary to maintain optimal well-being. This water-soluble vitamin is essential for the synthesis of collagen, which supports the integrity of the skin, blood vessels, cartilage, tendons, and ligaments. Additionally, its powerful antioxidant properties help fight oxidative stress and reduce inflammation, potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease.
Vitamin C deficiency can manifest itself in several ways, including dry skin, easy bruising, slow-healing wounds, and bleeding gums. Inadequate intake can also impair immune function and worsen conditions such as iron deficiency anemia and chronic fatigue. Ensuring an adequate intake of vitamin C through a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, or by supplementing when needed, is vital for maintaining health and preventing deficiencies.
The variety of supplements available, including ascorbic acid, liposomal vitamin C, and buffered vitamin C, allow individuals to choose the form that best suits their needs and preferences. While supplementation can be beneficial, it should complement a diet rich in natural sources of vitamin C. By incorporating these foods and supplements into your routine, you can support your body’s healing processes, boost your immune defenses, and maintain overall health and vitality.
